Shear walls are a critical component of modern structural engineering, particularly in regions prone to seismic activity. These vertical elements are designed to resist lateral forces such as wind and earthquakes, ensuring the stability and safety of buildings. Below is an overview of shear wall systems, their features, applications, and benefits:
What Are Shear Walls?
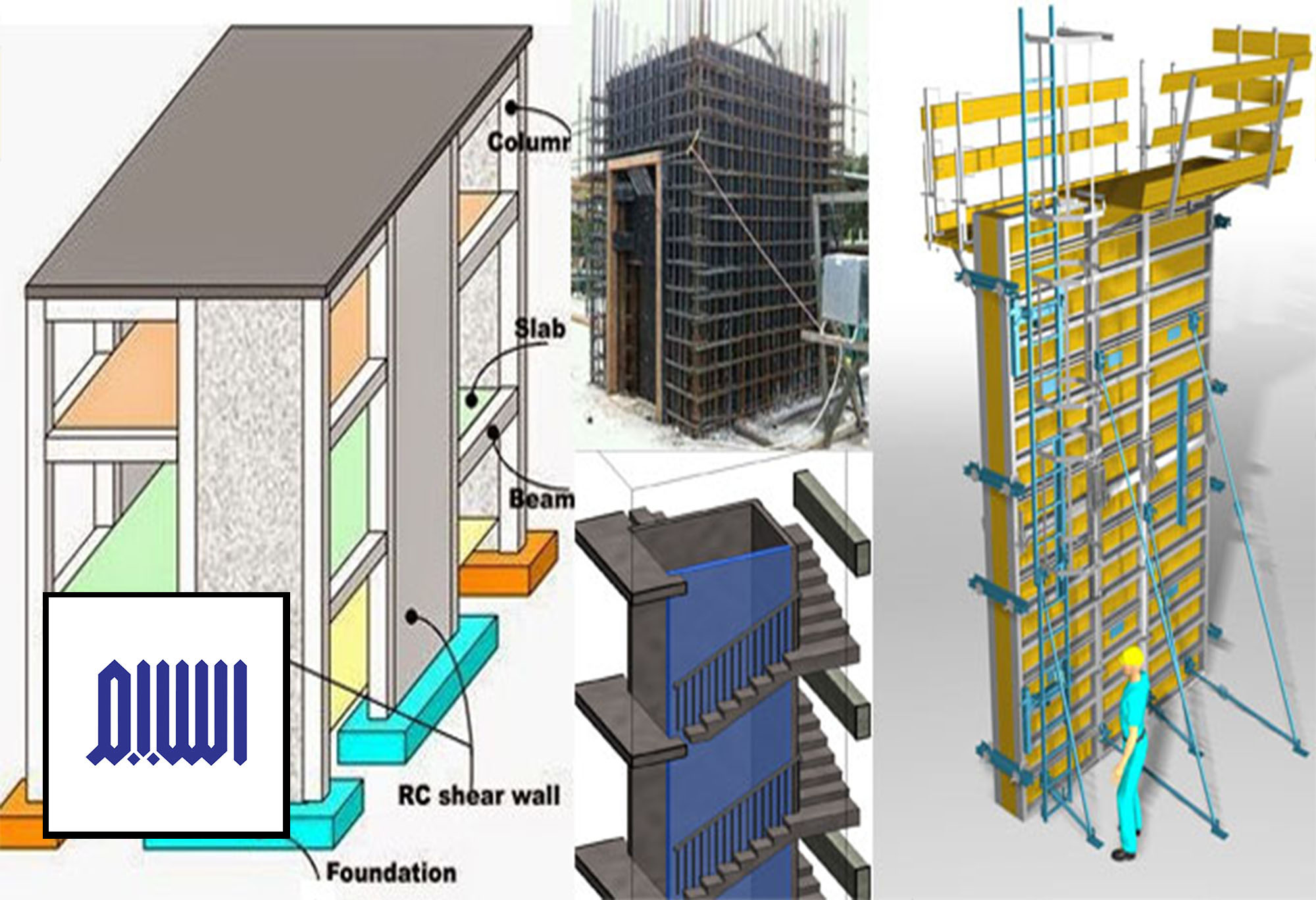
Shear walls are rigid vertical walls constructed within a building’s structure to counteract lateral loads caused by natural forces like wind and seismic activity. They are typically made of reinforced concrete, steel, or masonry and are strategically placed to distribute these forces evenly across the foundation.
Functions of Shear Walls
- Lateral Load Resistance
Shear walls are specifically designed to resist horizontal forces that can cause structural deformation during events like earthquakes or strong winds. - Structural Stability
By providing additional stiffness and strength, shear walls enhance the overall stability of a building, preventing excessive sway or collapse. - Load Distribution
These walls transfer lateral loads from the upper floors to the foundation, ensuring even distribution and minimizing stress on other structural elements. - Improved Safety
Shear walls significantly reduce the risk of structural failure, protecting both the building and its occupants during extreme conditions.
Advantages of Shear Walls
- Seismic Performance
Shear walls are highly effective in earthquake-prone areas, as they absorb and dissipate seismic energy, reducing damage to the structure. - Wind Resistance
In regions with high wind loads, shear walls provide the necessary resistance to prevent structural instability. - Space Efficiency
Unlike other bracing systems, shear walls do not require additional space, making them ideal for compact designs. - Durability
Made from robust materials like reinforced concrete, shear walls are long-lasting and require minimal maintenance. - Cost-Effectiveness
By enhancing structural integrity and reducing repair costs after natural disasters, shear walls offer a cost-effective solution for safe construction.
Applications of Shear Walls
- High-Rise Buildings
Shear walls are commonly used in tall structures to counteract lateral forces and ensure stability. - Residential Projects
In apartment complexes and housing developments, shear walls protect against seismic activity and wind loads. - Commercial Structures
Office buildings, shopping malls, and hotels utilize shear walls to maintain structural integrity under varying conditions. - Industrial Facilities
Factories and warehouses often incorporate shear walls to withstand heavy equipment vibrations and external forces. - Critical Infrastructure
Hospitals, schools, and government buildings rely on shear walls to ensure safety during emergencies.
Types of Shear Walls
- Reinforced Concrete Shear Walls
These are the most common type, offering high strength and durability. They are widely used in both residential and commercial projects. - Steel Plate Shear Walls
Ideal for lightweight structures, these walls use steel plates to provide flexibility and resistance. - Masonry Shear Walls
Constructed using bricks or concrete blocks, these walls are cost-effective and suitable for low-rise buildings. - Composite Shear Walls
Combining materials like concrete and steel, these walls offer enhanced performance and are used in specialized projects. - Coupled Shear Walls
These consist of two or more shear walls connected by beams or slabs, improving load distribution and structural stability.
Design and Construction of Shear Walls
- Planning and Analysis
Structural engineers analyze the building’s location, height, and environmental conditions to determine the optimal placement and design of shear walls. - Material Selection
High-quality materials such as reinforced concrete or steel are chosen based on the project’s requirements and budget. - Construction Process
- Formwork Installation : Molds are set up to shape the shear walls.
- Reinforcement Placement : Steel bars are placed within the formwork to enhance strength.
- Concrete Pouring : High-strength concrete is poured into the molds and allowed to cure.
- Quality Control : Rigorous testing ensures the walls meet safety and performance standards.
- Integration with Other Systems
Shear walls are integrated with beams, columns, and slabs to create a cohesive structural system.
Benefits of Using Shear Walls in Construction
- Enhanced Safety
Shear walls significantly improve a building’s ability to withstand natural disasters, protecting lives and property. - Improved Building Performance
By reducing lateral movement, shear walls enhance comfort and usability, especially in high-rise buildings. - Sustainability
The durability of shear walls reduces the need for repairs and replacements, contributing to sustainable construction practices. - Aesthetic Flexibility
Shear walls can be incorporated into various architectural designs without compromising functionality.
Why Choose Shear Wall Systems?
Shear walls are an essential feature of modern construction, particularly in areas with high seismic or wind risks. Their ability to enhance structural stability, safety, and performance makes them indispensable for a wide range of projects. Whether for residential, commercial, or industrial applications, shear walls provide reliable and innovative solutions.






0 Comments