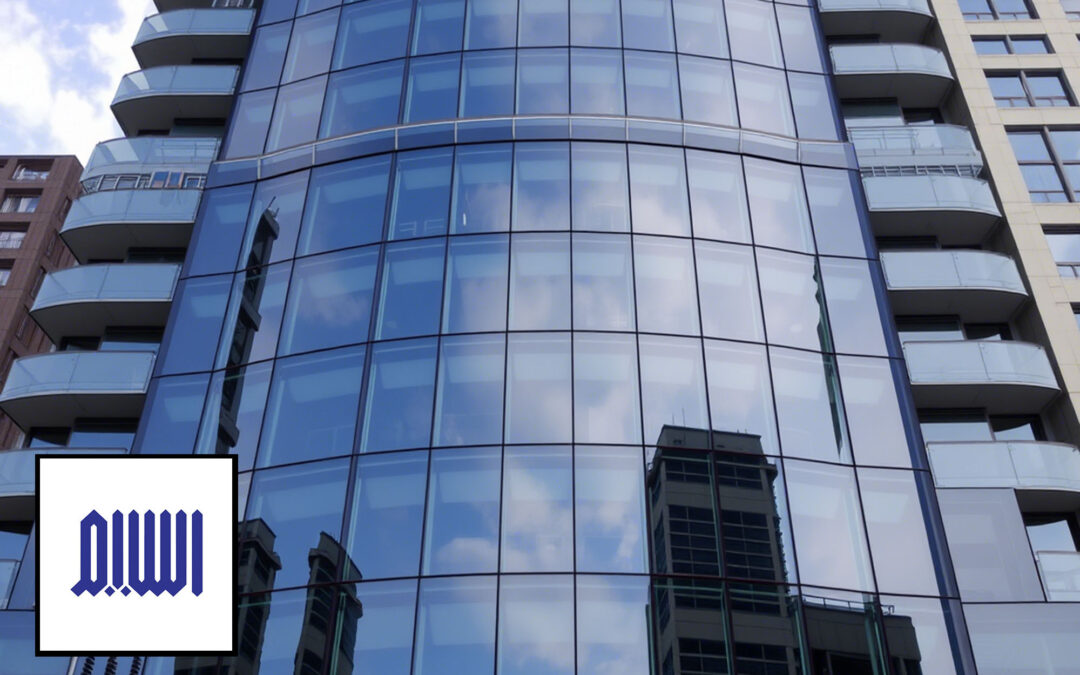
Glass is one of the most important building materials, playing a prominent role in the aesthetics, functionality, and safety of buildings. With advancements in technology, various types of architectural glass have been designed and produced, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. In this article, we will comprehensively examine the different types of architectural glass and their proper installation methods.
Types of Architectural Glass and Their Applications
- Flat Glass: The Classic Choice for Construction Projects
Flat glass, also known as window glass, is one of the most widely used types of architectural glass. It is produced in thicknesses ranging from 1.8 to 6 millimeters and is commonly used for windows, display cases, picture frames, and even glass doors. High-quality flat glass should be smooth, colorless, and free of bubbles. Due to its affordability and versatility, it is used in many buildings. - Frosted Glass: Privacy and Beauty Combined
Frosted glass is used to prevent direct visibility of objects behind the glass. It is created by sandblasting or treating the surface with hydrofluoric acid. Frosted glass is typically used in hospitals, bathrooms, and private spaces. In addition to maintaining privacy, it allows light to pass through effectively, making it an excellent choice for interior design. - Patterned Glass: Beauty Meets Functionality
Patterned glass is manufactured using textured rollers or decorative patterns. While it allows light to pass through, objects behind it are not clearly visible. This type of glass is often used in first-aid boxes, spaces requiring privacy, and modern interior designs. Produced in thicknesses of 3 to 4 millimeters, patterned glass adds a unique aesthetic to spaces due to its variety of designs. - Wired Glass: High Resistance to Fire and Impact
Wired glass is made by embedding a steel wire mesh between layers of glass. It is more resistant to fire and impact, and when broken, the pieces remain intact. Wired glass is commonly used in factories, garages, and roof coverings. Its high resistance makes it an ideal choice for hazardous environments. - Tinted Glass: A Blend of Beauty and Functionality
Tinted glass is produced by adding chemical compounds to the glass mixture or dipping white glass into colored liquids. It is used in display cases, exhibitions, and industrial buildings. In addition to its aesthetic appeal, tinted glass blocks harmful solar rays. Available in colors such as red, blue, and yellow, it serves as a decorative element in both interior and exterior building designs. - Tempered Glass: Safety and High Strength
Tempered glass is produced by heating the glass to approximately 700°C and then rapidly cooling it. This process increases its strength by 3 to 5 times. When broken, tempered glass shatters into small, harmless fragments. It is commonly used in display cases, glass doors, and side windows of vehicles. Due to its high safety, tempered glass is widely used in high-rise buildings and public spaces. - Double-Glazed Glass: Thermal and Acoustic Insulation
Double-glazed glass consists of two layers of glass with an air gap between them. These glasses provide thermal and acoustic insulation and are used in buildings such as airports, hotels, and hospitals. Double-glazed glass can reduce sound intensity by up to 50 decibels and helps save energy by minimizing heat transfer. - Laminated Glass: Safety and Impact Resistance
Laminated glass is made by combining two or more layers of glass with PVB interlayers. It is highly resistant to impact and breakage and is used in full-glass facades, soundproof recording studios, and anti-theft windows. Due to its strength and safety, laminated glass is widely used in modern buildings. - Bulletproof Glass: Security at Its Highest Level
Bulletproof glass is made from multiple layers of tempered or laminated glass. It is resistant to bullets and is used in banks, museums, and security-sensitive buildings. Due to its high resistance, bulletproof glass provides exceptional security and is commonly used in sensitive areas. - Reflective Glass: Reducing Energy Consumption
Reflective glass is produced with a metallic or metal oxide coating that reflects sunlight. It is effective in reducing heat and glare and is suitable for buildings exposed to intense sunlight. Reflective glass is widely used in sustainable and green buildings due to its energy-saving properties.
Methods of Installing Architectural Glass
- Cutting and Installing Glass
Glass cutting is performed using diamond blades. During installation, there should be a 2 to 3 millimeter gap between the frame and the glass. For installation in metal or wooden frames, padding or plastic strips are used. In aluminum frames, rubber strips are used to install the glass. These methods are popular due to their simplicity and speed. - Drilling and Polishing Glass
Diamond drill bits are used for drilling glass. Polishing is done to smooth sharp edges and prevent potential injuries. This process is carried out in factories and workshops using diamond sanding machines. - Installing Glass Tiles
Glass tiles are typically produced in sizes of 20×20 cm or 15×15 cm and are used for basement light wells. These tiles are installed using white cement mortar, and the gaps between them are filled with cement grout. This installation method is widely used due to its simplicity and aesthetic appeal. - Cleaning Glass
After installation, glass surfaces must be carefully cleaned. Thinner is used to remove leftover paint from painting, and specialized glass-cleaning machines can also be employed. This process is crucial for maintaining the beauty and functionality of the glass.
Conclusion
Architectural glass plays a vital role in the aesthetics, functionality, and safety of buildings, thanks to its diverse characteristics and applications. Choosing the right type of glass and ensuring proper installation can improve quality of life and reduce energy costs. With technological advancements, new types of glass, such as smart glass and solar glass, are being developed, promising a bright future for the construction industry.






0 Comments